Difference between revisions of "Translation"
From Robotics
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
For further information about vector addition and examples, please have a look at the article about [[Simple arithmetic operations|simple arithmetic vector operations]]. | For further information about vector addition and examples, please have a look at the article about [[Simple arithmetic operations|simple arithmetic vector operations]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Article]] | [[Category:Article]] | ||
[[Category:Transformations]] | [[Category:Transformations]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:31, 24 November 2017
| ← Back: Transformations | Overview: Transformations | Next: Rotation → |
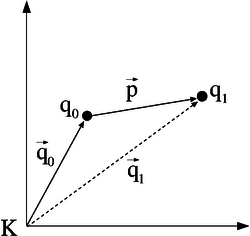
Translation is the easiest kind of transformation. Translating a point 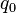 means that it is shifted by a translation vector. So the translation vector
means that it is shifted by a translation vector. So the translation vector 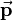 is added to the position vector
is added to the position vector 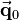 of
of 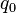 . The position vector
. The position vector 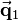 of the resulting transformed point
of the resulting transformed point 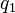 is calculated as follows:
is calculated as follows:
The figure on the right shows an example in two-dimensional space. In robotics usually three dimensions are regarded. Considering the particular components of the vectors, a translation looks as follows:
For further information about vector addition and examples, please have a look at the article about simple arithmetic vector operations.
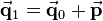
![\left[\begin{array}{c}
x_1\\
y_1\\
z_1
\end{array}\right]=
\left[\begin{array}{c}
x_0\\
y_0\\
z_0
\end{array}\right]+
\left[\begin{array}{c}
p_x\\
p_y\\
p_z
\end{array}\right]=
\left[\begin{array}{c}
x_0+p_x\\
y_0+p_y\\
z_0+p_z
\end{array}\right]](/wiki/robotics/images/math/1/e/6/1e66b61668e846900c7121715b5fa419.png)