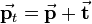Difference between revisions of "Translation"
From Robotics
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Navigation|before=[[ | + | {{Navigation|before=[[Transformations]]|overview=[[Transformations]]|next=[[Rotation]]}} |
[[File:translation1.png|right|250px]] | [[File:translation1.png|right|250px]] | ||
Revision as of 16:38, 26 May 2014
| ← Back: Transformations | Overview: Transformations | Next: Rotation → |
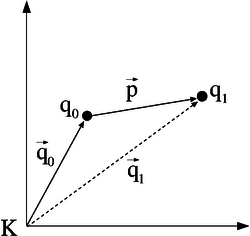
Translation is the easiest kind of transformation. Translating a point 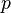 means that it is shifted by a translation vector. So the translation vector
means that it is shifted by a translation vector. So the translation vector 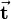 is added to the position vector
is added to the position vector 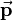 of
of 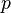 . The position vector
. The position vector 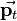 of the resulting transformed point
of the resulting transformed point 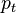 is calculated as follows:
is calculated as follows:
For further information about vector addition and examples, please have a look at the article about simple arithmetic vector operations.
An alternative way to describe a translation is the matrix notation.