Difference between revisions of "Inverse transformation"
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
& &\mathbf{R}_i& \qquad\qquad \vec{\mathbf{p}}_i\\ | & &\mathbf{R}_i& \qquad\qquad \vec{\mathbf{p}}_i\\ | ||
\end{align}</math> | \end{align}</math> | ||
| − | + | So the inverse of a homogeneous transformation matrix is defined as:<br/> | |
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | \mathbf{T}^{-1}= | ||
| + | \left[\begin{array}{ccc|c} | ||
| + | & & & \\ | ||
| + | & \mathbf{R} & & \vec{\mathbf{p}}\\ | ||
| + | & & & \\ \hline | ||
| + | 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 | ||
| + | \end{array}\right]^{-1}= | ||
| + | \left[\begin{array}{ccc|c} | ||
| + | & & & \\ | ||
| + | & \mathbf{R}_i & & \vec{\mathbf{p}}_i\\ | ||
| + | & & & \\ \hline | ||
| + | 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 | ||
| + | \end{array}\right]= | ||
| + | \left[\begin{array}{ccc|c} | ||
| + | & & & \\ | ||
| + | & \mathbf{R}^T & & -\mathbf{R}^T\vec{\mathbf{p}}\\ | ||
| + | & & & \\ \hline | ||
| + | 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 | ||
| + | \end{array}\right] | ||
| + | </math> | ||
[[Category:Article]] | [[Category:Article]] | ||
[[Category:Transformations]] | [[Category:Transformations]] | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 17 June 2014
| ← Back: Combinations of transformations | Overview: Transformations | Next: ??? → |
Let 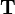 be a general homogeneous transformation matrix. The inverse transformation
be a general homogeneous transformation matrix. The inverse transformation 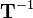 corresponds to the transformation that reverts the rotation and translation effected by
corresponds to the transformation that reverts the rotation and translation effected by 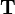 . If a vector is pre-multiplied by
. If a vector is pre-multiplied by 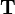 and subsequently pre-multiplied by
and subsequently pre-multiplied by 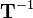 , this results in the original coordinates because
, this results in the original coordinates because 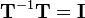 and multiplication with the identity matrix does not change anything (see transformations).
and multiplication with the identity matrix does not change anything (see transformations).
The general homogeneous transformation matrix 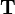 for three-dimensional space consists of a 3-by-3 rotation matrix
for three-dimensional space consists of a 3-by-3 rotation matrix 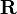 and a 3-by-1 translation vector
and a 3-by-1 translation vector 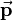 combined with the last row of the identity matrix:
combined with the last row of the identity matrix:
As stated in the article about homogeneous coordinates, multiplication with 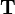 is equivalent in cartesian coordinates to applying the rotation matrix
is equivalent in cartesian coordinates to applying the rotation matrix 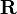 first and then translating the coordinates by
first and then translating the coordinates by 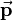 :
:
The equation above is now solved for 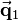 . Here the fact is used, that the inverse of 3-by-3 rotation matrices equals the transpose of the matrix:
. Here the fact is used, that the inverse of 3-by-3 rotation matrices equals the transpose of the matrix:
So the inverse of a homogeneous transformation matrix is defined as:
![\mathbf{T}=
\left[\begin{array}{ccc|c}
& & & \\
& \mathbf{R} & & \vec{\mathbf{p}}\\
& & & \\ \hline
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right]](/wiki/robotics/images/math/1/3/2/1327593f05795df92e5c12f1a1a27f84.png)
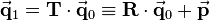
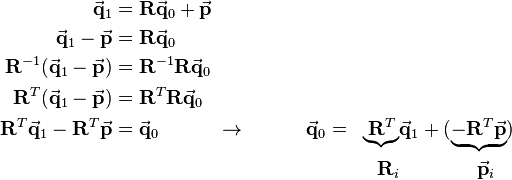
![\mathbf{T}^{-1}=
\left[\begin{array}{ccc|c}
& & & \\
& \mathbf{R} & & \vec{\mathbf{p}}\\
& & & \\ \hline
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right]^{-1}=
\left[\begin{array}{ccc|c}
& & & \\
& \mathbf{R}_i & & \vec{\mathbf{p}}_i\\
& & & \\ \hline
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right]=
\left[\begin{array}{ccc|c}
& & & \\
& \mathbf{R}^T & & -\mathbf{R}^T\vec{\mathbf{p}}\\
& & & \\ \hline
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right]](/wiki/robotics/images/math/7/f/b/7fbdbf0c44d5f9e1ed43f0f611797bf0.png)