Difference between revisions of "Inverse transformation"
From Robotics
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Navigation|before=[[Combinations of transformations]]|overview=[[Transformations]]|next=[[???]]}} | {{Navigation|before=[[Combinations of transformations]]|overview=[[Transformations]]|next=[[???]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | A general homogeneous transformation matrix <math>\mathbf{T}</math> for three-dimensional space consists of a 3-by-3 rotation matrix <math>\mathbf{R}</math> and a 3-by-1 translation vector <math>\vec{\mathbf{p}}</math> combined with the last row of the identity matrix:<br/> | ||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | \mathbf{T}= | ||
| + | \left[\begin{array}{ccc|c} | ||
| + | & & & \\ | ||
| + | & \mathbf{R} & & \vec{\mathbf{p}}\\ | ||
| + | & & & \\ \hline | ||
| + | 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 | ||
| + | \end{array}\right] | ||
| + | </math> | ||
[[Category:Article]] | [[Category:Article]] | ||
[[Category:Transformations]] | [[Category:Transformations]] | ||
Revision as of 13:42, 17 June 2014
| ← Back: Combinations of transformations | Overview: Transformations | Next: ??? → |
A general homogeneous transformation matrix 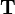 for three-dimensional space consists of a 3-by-3 rotation matrix
for three-dimensional space consists of a 3-by-3 rotation matrix 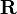 and a 3-by-1 translation vector
and a 3-by-1 translation vector 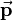 combined with the last row of the identity matrix:
combined with the last row of the identity matrix:
![\mathbf{T}=
\left[\begin{array}{ccc|c}
& & & \\
& \mathbf{R} & & \vec{\mathbf{p}}\\
& & & \\ \hline
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right]](/wiki/robotics/images/math/1/3/2/1327593f05795df92e5c12f1a1a27f84.png)