Difference between revisions of "MATLAB: Vector algebra"
From Robotics
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
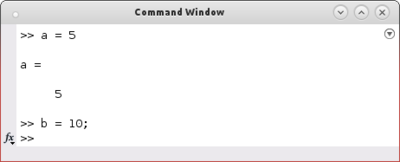
| − | In MATLAB you do not not have to declare a variable and its type. The type of a variable is specified through its initialization. So you choose a name for the variable and use the equal sign to initialize it. | + | In MATLAB you do not not have to declare a variable and its type. The type of a variable is specified through its initialization. So you choose a name for the variable and use the equal sign to initialize it. If no semicolon is used at the end of a command, MATLAB gives feedback about the initialized variable. Otherwise no output is generated. '''Scalar values''' for example are initialized like follows: |
| − | [[File:matlab-va-scalar.png| | + | |
| + | :[[File:matlab-va-scalar.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
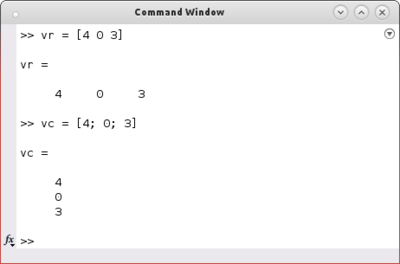
| + | An '''n-dimensional vector''' is created by typing the n components in rectangular brackets. Separation of the values with space leads to a row vector while values separated with a semicolon result in a column vector. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:matlab-va-vector.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
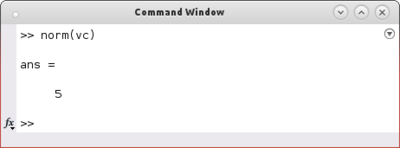
| + | To compute the '''magnitude of a vector''' use the command ''norm'': | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:matlab-va-vector-norm.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:MATLAB]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Vectors]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:02, 26 September 2014
| ← Previous: Overview | Next: Unit vectors → |
In MATLAB you do not not have to declare a variable and its type. The type of a variable is specified through its initialization. So you choose a name for the variable and use the equal sign to initialize it. If no semicolon is used at the end of a command, MATLAB gives feedback about the initialized variable. Otherwise no output is generated. Scalar values for example are initialized like follows:
An n-dimensional vector is created by typing the n components in rectangular brackets. Separation of the values with space leads to a row vector while values separated with a semicolon result in a column vector.
To compute the magnitude of a vector use the command norm: