Difference between revisions of "Assigning coordinate frames"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Navigation|before=[[Denavit-Hartenberg Convention]]|overview=[[Denavit-Hartenberg Convention]]|next=[[Denavit-Hartenberg parameters]]}} | {{Navigation|before=[[Denavit-Hartenberg Convention]]|overview=[[Denavit-Hartenberg Convention]]|next=[[Denavit-Hartenberg parameters]]}} | ||
| − | To be able to determine the spatial relationship or transformation, respectively, between the links of a manipulator, local coordinate frames have to assigned to them first. There are several rules that have to be observed when assigning coordinate frames following the Denavit-Hartenberg convention. | + | To be able to determine the spatial relationship or transformation, respectively, between the links of a manipulator, local coordinate frames have to assigned to them first. There are several rules that have to be observed when assigning coordinate frames following the Denavit-Hartenberg convention. The first rule is, that the manipulator has to be moved to its zero position. So all the joints or their joint parameters, respectively, have to be set to zero. Then the coordinate frames are assigned regarding the zero position. |
===Notation=== | ===Notation=== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Following the above notation, a coordinate frame is attached to each end of a link at the corresponding joint. The orientation of the coordinate frames depends on the joint and on the prior frame. There is one rule, that is always valid. This is, that the <math>z</math>-axis of a coordinate frame is always pointing in the direction of the main axis of the related joint. Like can be seen in the figure on the left, the main axis of a prismatic joint is the axis along which the displacement in positive direction is applied. For a revolute joint, the main axis is the rotation axis. The direction of the rotation axis and so of the main axis is depending on the positive rotation direction. When you hold your right hand like shown on the right and point your thumb in the direction of the rotation axis, the four other fingers indicate the rotation direction for positive angles. So the right hand can be used to determine the direction of the main axis. In the figure on the left, the thumb of the right hand has to point upwards, so that the 4 fingers correspond to the direction of the arrow indicating the positive rotation direction. Thus the main axis is directed upwards as well. | Following the above notation, a coordinate frame is attached to each end of a link at the corresponding joint. The orientation of the coordinate frames depends on the joint and on the prior frame. There is one rule, that is always valid. This is, that the <math>z</math>-axis of a coordinate frame is always pointing in the direction of the main axis of the related joint. Like can be seen in the figure on the left, the main axis of a prismatic joint is the axis along which the displacement in positive direction is applied. For a revolute joint, the main axis is the rotation axis. The direction of the rotation axis and so of the main axis is depending on the positive rotation direction. When you hold your right hand like shown on the right and point your thumb in the direction of the rotation axis, the four other fingers indicate the rotation direction for positive angles. So the right hand can be used to determine the direction of the main axis. In the figure on the left, the thumb of the right hand has to point upwards, so that the 4 fingers correspond to the direction of the arrow indicating the positive rotation direction. Thus the main axis is directed upwards as well. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === | ||
[[Category:Article]] | [[Category:Article]] | ||
[[Category:Denavit-Hartenberg]] | [[Category:Denavit-Hartenberg]] | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 30 October 2015
| ← Back: Denavit-Hartenberg Convention | Overview: Denavit-Hartenberg Convention | Next: Denavit-Hartenberg parameters → |
To be able to determine the spatial relationship or transformation, respectively, between the links of a manipulator, local coordinate frames have to assigned to them first. There are several rules that have to be observed when assigning coordinate frames following the Denavit-Hartenberg convention. The first rule is, that the manipulator has to be moved to its zero position. So all the joints or their joint parameters, respectively, have to be set to zero. Then the coordinate frames are assigned regarding the zero position.
Notation
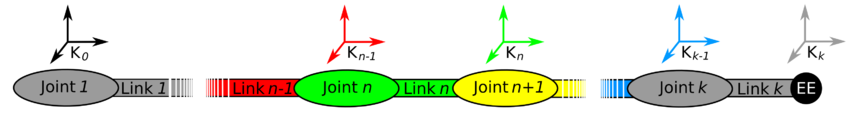
The notation of the links and joints is shown in the figure below. A manipulator consists of 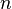 links that are connected with
links that are connected with 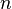 joints. The links correspond to the rigid parts of an arm and the joints are the flexible connections between them. A joint is always assigned to the proximate link. So a link
joints. The links correspond to the rigid parts of an arm and the joints are the flexible connections between them. A joint is always assigned to the proximate link. So a link 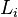 is connected with its joint
is connected with its joint 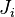 to the end of link
to the end of link 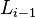 . The proximate link
. The proximate link 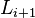 is then mounted to the end of
is then mounted to the end of 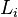 via its joint
via its joint 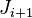 . The first link
. The first link 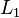 is mounted on the base via joint
is mounted on the base via joint 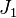 . So the base is actually link
. So the base is actually link 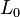 but does not directly belong to the manipulator. The end of the last link
but does not directly belong to the manipulator. The end of the last link 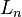 corresponds to the end-effector.
corresponds to the end-effector.
The coordinate frames are always attached to the end of the links at the distal joints. The first coordinate frame, indexed 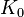 , is the base or reference frame and attached to the base in joint
, is the base or reference frame and attached to the base in joint 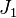 . The next frame is
. The next frame is 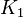 at the end of link
at the end of link 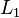 in joint
in joint 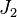 followed by
followed by 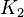 at the end of
at the end of 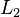 and so on. The coordinate frame
and so on. The coordinate frame 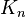 of the last link is finally attached to the end of of the manipulator and so to the end-effector.
of the last link is finally attached to the end of of the manipulator and so to the end-effector.
Main joint axes
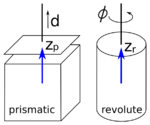
Following the above notation, a coordinate frame is attached to each end of a link at the corresponding joint. The orientation of the coordinate frames depends on the joint and on the prior frame. There is one rule, that is always valid. This is, that the 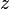 -axis of a coordinate frame is always pointing in the direction of the main axis of the related joint. Like can be seen in the figure on the left, the main axis of a prismatic joint is the axis along which the displacement in positive direction is applied. For a revolute joint, the main axis is the rotation axis. The direction of the rotation axis and so of the main axis is depending on the positive rotation direction. When you hold your right hand like shown on the right and point your thumb in the direction of the rotation axis, the four other fingers indicate the rotation direction for positive angles. So the right hand can be used to determine the direction of the main axis. In the figure on the left, the thumb of the right hand has to point upwards, so that the 4 fingers correspond to the direction of the arrow indicating the positive rotation direction. Thus the main axis is directed upwards as well.
-axis of a coordinate frame is always pointing in the direction of the main axis of the related joint. Like can be seen in the figure on the left, the main axis of a prismatic joint is the axis along which the displacement in positive direction is applied. For a revolute joint, the main axis is the rotation axis. The direction of the rotation axis and so of the main axis is depending on the positive rotation direction. When you hold your right hand like shown on the right and point your thumb in the direction of the rotation axis, the four other fingers indicate the rotation direction for positive angles. So the right hand can be used to determine the direction of the main axis. In the figure on the left, the thumb of the right hand has to point upwards, so that the 4 fingers correspond to the direction of the arrow indicating the positive rotation direction. Thus the main axis is directed upwards as well.